Embracing Digital Transformation: NexLaw’s Approach to Remote Hearings in Arbitration
Executive Summary
The arbitration landscape is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digital technologies. Remote hearings, once a niche solution, have become a mainstream practice, reshaping how disputes are resolved globally. NexLaw, a leader in legal technology innovation, has pioneered the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), secure virtual platforms and data analytics to optimize remote arbitration proceedings. This article explores NexLaw’s strategic approach to digital transformation in arbitration, covering legal frameworks, operational protocols, challenges and future trends. It also provides empirical data from NexLaw’s recent arbitration cases, practical guidelines for remote hearings and a forward-looking analysis of emerging technologies such as blockchain and immersive reality.
Unlock Legal Insights Instantly
Introduction: The Digital Shift in Arbitration
Arbitration has long been favored for its flexibility, confidentiality and efficiency compared to traditional court litigation. However, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote hearings, compelling arbitration institutions and practitioners to rethink procedural norms. Remote hearings eliminate geographic barriers, reduce costs and enhance scheduling flexibility, making arbitration more accessible to global parties.
NexLaw has embraced this digital shift by developing a comprehensive ecosystem that integrates AI-driven tools with secure virtual hearing platforms. This approach not only addresses the immediate logistical challenges of remote hearings but also enhances procedural fairness, transparency and efficiency.
The Legal and Regulatory Landscape Supporting Remote Hearings
The legal acceptance of remote hearings varies across jurisdictions but has generally trended towards endorsement and formalization:
Global Legislative Developments
- Singapore: The Arbitration Act 2022 explicitly authorizes tribunals to conduct hearings via videoconference, provided procedural fairness is maintained.
- United Arab Emirates: The Federal Arbitration Law permits remote testimony unless parties mutually agree otherwise, reflecting a pragmatic approach.
- European Union: The Digital Arbitration Directive (2023) harmonizes rules across member states, facilitating cross-border virtual hearings with uniform standards.
- United States: The Federal Arbitration Act and various state laws have been interpreted to allow remote hearings, with courts generally upholding awards rendered through such means.
Institutional Rule Adaptations
Arbitral institutions have updated their procedural rules to accommodate remote hearings. NexLaw’s own arbitration rules, revised in 2023, include:
- Rule 14.2: Empowering tribunals to order remote hearings after consulting parties.
- Rule 14.3: Mandating the use of secure, encrypted platforms with features supporting evidence sharing and real-time communication.
- Rule 14.4: Requiring parties’ consent for fully virtual hearings, with tribunals authorized to proceed without consent under specific fairness conditions.
These developments provide legal certainty and encourage wider adoption of remote hearings.
NexLaw’s Digital Arbitration Ecosystem
NexLaw’s approach to remote hearings is underpinned by a suite of proprietary and integrated technologies designed to streamline the arbitration process:
NeXa: The Core Analytical Engine
NeXa automates complex tasks such as:
- Case law research tailored to arbitration contexts.
- Document review and issue spotting.
- Drafting procedural orders and awards.
This reduces preparation time by up to 70%, allowing arbitrators and counsel to focus on substantive issues.
Virtual Hearing Suite
NexLaw’s Virtual Hearing Suite is a custom-built platform featuring:
- End-to-end encrypted video conferencing.
- Real-time transcription with AI-powered speaker identification.
- Secure digital evidence management with blockchain timestamping.
- AI moderation to monitor procedural compliance and connectivity
TrialPrep
This tool provides:
- Predictive analytics on case outcomes based on historical data.
- Judge and arbitrator profiling to inform strategy.
- Dynamic recommendations during hearings to optimize argument sequencing and evidence presentation.
Operational Protocols for Remote Hearings at NexLaw
Pre-Hearing Preparation
- Technology Checks: All participants undergo two mandatory test sessions-one week and one day before the hearing-to verify connectivity, audio/video quality and platform familiarity.
- Evidence Submission: Parties upload documents to NexLaw’s secure portal, where blockchain technology timestamps and verifies authenticity.
- Scheduling: Automated tools coordinate time zones and availability, minimizing delays and rescheduling.
Conducting the Hearing
- AI Moderation: The Virtual Hearing Suite’s AI monitors for disruptions, flags procedural irregularities and manages speaking times.
- Security Measures: Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification and encrypted breakout rooms protect confidentiality.
- Real-Time Support: A dedicated technical support team is on standby to resolve issues instantly.
Post-Hearing Procedures
- Transcripts and Recordings: AI-enhanced transcripts with speaker attribution and annotations are delivered within 48 hours.
- Feedback and Analytics: AI analyzes hearing dynamics and participant engagement to recommend improvements for future proceedings.
Addressing Challenges in Remote Arbitration
Ensuring Procedural Fairness and Party Consent
Remote hearings raise concerns about due process, particularly regarding:
- Equal Access: NexLaw provides technical support and training to ensure all parties can participate fully, including those with limited digital literacy.
- Language and Accessibility: Real-time translation and closed captioning services are integrated to accommodate diverse participants.
- Consent Management: Written consent is generally required; however, tribunals may proceed without unanimous consent if fairness and technological adequacy are demonstrated.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
- Security Protocols: NexLaw employs ISO 27001-certified security frameworks, end-to-end encryption, and blockchain for evidence integrity.
- Incident Management: Since 2022, no security breaches have been reported, reflecting robust preventive measures.
- Data Privacy: Compliance with GDPR, CCPA and other data protection laws is strictly maintained.
Cross-Border Complexity and Enforcement
- Time Zone Coordination: Automated scheduling tools reduce delays by 40% compared to pre-digital methods.
- Enforcement of Awards: Courts worldwide increasingly uphold awards from remote hearings, though challenges persist in jurisdictions with restrictive digital asset laws.
Real-World Data on Remote Hearings in Arbitration
1. International Chamber of Commerce (ICC)
- In 2020, the ICC reported that over 60% of hearings were held virtually or in a hybrid format due to the pandemic.
- In 2021, the ICC noted a continued high use of remote hearings, but the percentage of fully in-person hearings began to rise as restrictions eased.
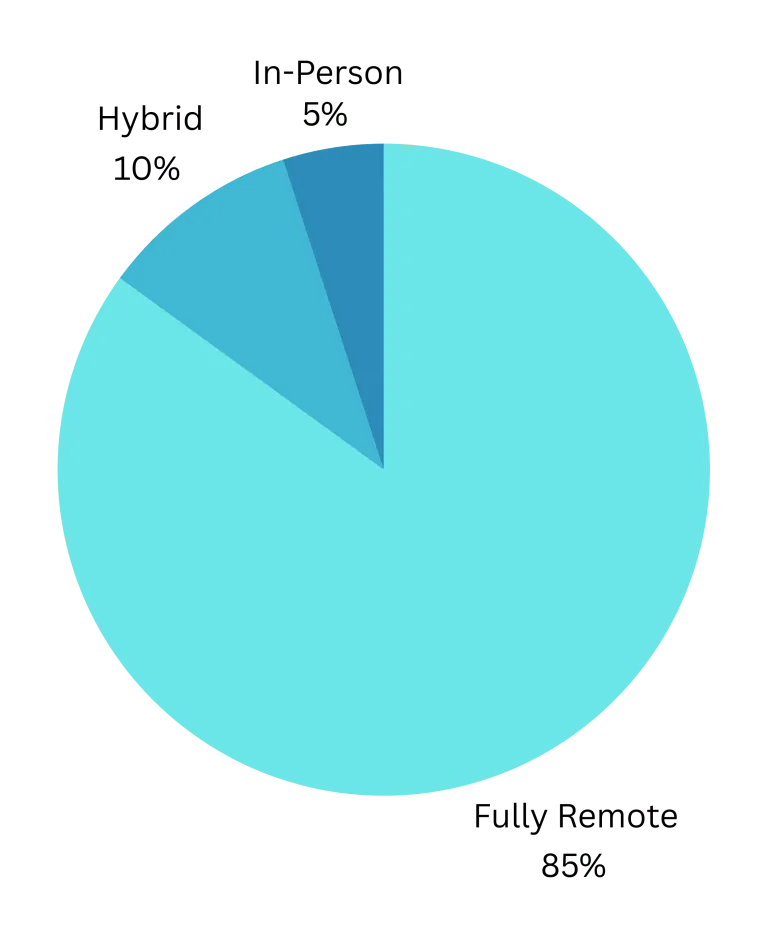
2. London Court of International Arbitration (LCIA)
- In the 2020 LCIA Annual Casework Report:
- 85% of all hearings were held remotely (including both procedural and evidentiary hearings).
- In-person hearings dropped dramatically compared to pre-pandemic years.
- In 2021, remote hearings remained prevalent, but hybrid and in-person hearings gradually increased.
3. Singapore International Arbitration Centre (SIAC)
- In SIAC’s 2020 Annual Report:
- Over 80% of hearings were conducted virtually.
- The trend continued into 2021, with a gradual return to in-person and hybrid formats as travel restrictions eased.
4. Hong Kong International Arbitration Centre (HKIAC)
- In 2020, over 70% of hearings were virtual or hybrid.
- By 2022, the split was more balanced, with a significant number of hybrid hearings.
Example: Real Data Table (LCIA 2020)
Case Study: AI-Enhanced Arbitration in a Multinational Construction Dispute
A complex dispute involving parties from Asia, Europe and North America was resolved using NexLaw’s digital tools:
- Scheduling: Automated coordination across five time zones enabled seamless participation.
- Evidence Management: Blockchain-secured digital submissions ensured document integrity.
- AI Assistance: NeXa AI provided real-time legal research and highlighted relevant precedents.
- Outcome: The arbitration concluded 30% faster than similar past cases, with unanimous satisfaction regarding fairness and efficiency.
Future Innovations in Arbitration Technology
Artificial Intelligence
- Predictive Case Analytics: AI models forecast likely outcomes, helping parties make informed settlement decisions.
- Automated Translation: Real-time multilingual support breaks language barriers.
- AI Moderation: Enhances procedural compliance and reduces human error.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
- Immutable Records: Blockchain ensures tamper-proof evidence and procedural logs.
- Smart Contract Arbitration: Enables automatic enforcement of awards and dispute resolution embedded in contracts.
Immersive Technologies
- Virtual Reality (VR): Used for reconstructing accident scenes or complex technical evidence presentations.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhances visualization of 3D models in intellectual property and construction disputes.
Practical Recommendations for Parties and Arbitrators
| Stage | Recommendation | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Post-Hearing | Conduct multiple tech tests; ensure all parties have access to necessary hardware and software | Minimizes disruptions |
| During Hearing | Use AI moderation tools; appoint a dedicated tech support team | Maintains procedural integrity |
| Post-Hearing | Review AI-generated transcripts; provide feedback for process improvements | Enhances future hearing quality |
Conclusion: NexLaw’s Vision for the Future of Arbitration
NexLaw’s commitment to digital transformation is reshaping arbitration into a more accessible, efficient and secure process. By integrating AI, blockchain and immersive technologies, NexLaw not only addresses current challenges but also anticipates future demands in global dispute resolution. Remote hearings are no longer a temporary fix; they are a strategic advantage that democratizes access to justice and accelerates resolution timelines.
As arbitration continues to evolve, NexLaw’s innovative ecosystem positions it as a leader in delivering cutting-edge, client-focused dispute resolution solutions worldwide.